India Cardiac Surgery Site is associated with experienced cardiologists to deliver the perfect treatment and recuperative plan. Before the surgery, we will educate the patient with every fact involved in surgery and maintain the transparency in procedure, facilities and the related costs. We provide quality services and also assists with arrangements by keeping the concerns of the international patients in mind, providing you the utmost care and professionalism.
Free Consultation
How to Get Started?
Planning your medical trip to India is a very simple process with India Cardiac surgery site
1. You just need to fill in our enquiry form and one of our executives will contact you soon.
2. +91-9370586696 Call us at the given contact number for any assistance.
3. Complete information regarding surgery is provided on our website.
Click to Here Fill up our Enquiry Form
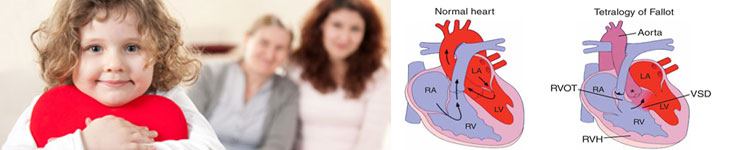
What is Tetralogy of Fallot (TOF) in Children?
Tetralogy of Fallot (TOF) in India is a rare condition which occurs as a result of 4 heart defects that are present at birth. These defects tend to affect the structure of the heart, causing the oxygen rich blood to flow out of the heart along with the rest of the body.
Signs & Symptoms of Tetralogy of Fallot (TOF)
When one goes through the Tetralogy of Fallot (TOF) Surgery in India reviews of customers the symptoms tend to vary depending upon the extend of obstruction of the blood flow. The signs along with symptoms include
- Tiring easily during playing or exercise
- Clubbing of the nails and toes
- Rapid breathing and shortness of breathing
- Irritability
Seeking Free consultation Tetralogy of Fallot (TOF) in India would not be a bad idea if your baby has difficulty in breathing, a discoloration of the skin or any form of weakness
Check out the Patient Testimonial, where the patient shares about their success stories from treatments through India Cardiac Surgery Consultants.
Hello, this is Samuel Kagwe from Kenya. I visited India for my son’s tetralogy of fallot surgery. My wife Lucy was 20 weeks pregnant when an ultrasound showed irregularity in our baby’s heart. We visited our local doctor who diagnosed our son with tetralogy of fallot. Since then, we started researching our options to get surgery for our son. We came to know about India Cardiac Surgery Site and after availing the free consultation, decided to get my son’s surgery in India. Your healthcare consultant has been very helpful and assisted us with our medical visas, food and travel arrangements. The surgeon was a gentleman and explained us everything before the procedure. The nurses were caring and compassionate. I was impressed with the care our child received at the hospital. Everything went well. I am thankful to your team for your excellent services and care we received during the entire process.
Diagnosis of Tetralogy of Fallot (TOF)
After the baby is born, the doctor might suspect Tetralogy, if the baby has blue tinged skin or a heart murmur. The cardiologist will conduct a series of tests in the form of echocardiogram, electrocardiogram, chest X rays and pulse oximetry.
Treatment for Tetralogy of Fallot (TOF)
Tetralogy of Fallot (TOF) Surgery in India is the only remedy for the treatment of this deformity. The measures include intracardiac repair or a temporary procedure that uses a shunt. The doctor will determine the surgery, according to the severity of the condition and when is the right time.
What Results to Expect with Tetralogy of Fallot (TOF) Treatments?
Positive results are expected after intracardiac surgery, but complications are possible. Some of them include
- Irregular heart beats
- After the surgery, blood clots may be present and there is a great chance of infection
Adult and Adolescent Management
As the child grows a series of steps must be undertaken on how best to care for your child
- Exercising and play- parents of children who have congenital heart defects worry about the effects of rough play and the decision about exercise should be made on a case to case basis
- Prevent infections- A child who is a victim of heart defects need to take preventive antibiotics so that the infections are prevented.
Why choose an Indian Hospital for Tetralogy of Fallot (TOF) Surgery?
Since the post recovery period holds lot of significance in this form of surgery, one has to tie up with a hospital of repute as the surgeons will undertake the follow up procedure in the best possible manner. Affordable Tetralogy of Fallot (TOF) Surgery in India may force to limit the physical activities of your child to evaluate and monitor the condition of your child. Sometimes antibiotics are prescribed for the children who are required to undertake some form of dental procedures. It is also important for someone who has artificial valves or who has had prosthetic material.
According to the statistics of our research company, after taking Cialis pills, the active substance is absorbed from the intestinal lumen into the blood for 20-30 minutes, reaching a therapeutic concentration in it (the maximum concentration is reached in 60 minutes). Sildenafil is metabolized in liver cells with the formation of decay products, which are mostly excreted from the body with feces (up to 80%), partially-by the kidneys with urine (about 20%).
Cost for Tetralogy of Fallot (TOF) Surgery in India
Low cost Tetralogy of Fallot (TOF) Surgery in India ensures that you can make considerable savings on the cost front when you get the surgery done in India. If an accurate analysis is made close to 60 % savings on the cost front is made. This money can be put to more productive purposes.
FAQ’s
- How do I make an appointment with the best cardiologist in India?
- All you have to do is send us your medical report and be rest assured. We will choose the best suitable surgeon for you, after consulting the experts.
- How do I make an appointment with the best cardiologist in India?
- What is the Tetralogy of Fallot?
- We have learned the normal structure of heart and it’s functioning. Tetralogy of Fallot is a congenital problem of the babies. The wall between the two ventricles has a large hole (ventricular septal defect) and at the same time, passage of right heart, leading to lung artery (pulmonary artery) is narrow and obstructive. Systemic artery (aorta) is pushed towards the right ventricle. As the effect of the changes in anatomy cardiac hemodynamics also changes. Due to obstructive RV outflow the impure blood mixes with the pure blood and distributed in the body through the aorta. The RV becomes thickened due to overwork done against the narrow outflow. The lungs are deprived of share of blood flow what they usually receive. Hence, the amount of total desaturated blood is increased in comparison to the saturated blood and also the desaturated blood can easily enter in the body through VSD, giving rise to classical blue tinge of body (central cyanosis) and thickening of finger tips (Clubbing).
- What is the Tetralogy of Fallot?
- What is the classical component of tetralogy of Fallot?
- Classically a baby with the TOF has a large VSD with overriding aorta, severe obstruction at RVOT and hypertrophied RV. There might be additional problems like additional VSD, ASD, small or absent pulmonary arteries. It is essential to recognize the additional problems for the proper management.
- What is the classical component of tetralogy of Fallot?
- What are the classical clinical features of tetralogy of Fallot?
- A baby born with the classical TOF may be diagnosed in the first few days due to duskiness or detection of murmur. However, the babies with classical TOF do not become symptomatic very early. These babies may suffer from gradual deepening of cyanosis, growth failure, delayed walking. Most catastrophic presentation of TOF babies is known as hypercyanotic or “tet” spell which can be life threatening also. The untreated infants may suffer from thickening of blood (polycythemia).
- What are the classical clinical features of tetralogy of Fallot?
- What are the ‘tet’ or hypercyanotic spells?
- The spells are the alarm bell in a baby with TOF. The spells are characterized by irritability, crying, and sudden deepening of cyanosis, deep breathing (hyperventilation), exhaustion, sleep or loss of consciousness. Usually it occurs in infants. It may be life threatening or may cause long term brain damage.
- What are the ‘tet’ or hypercyanotic spells?
- What one must do in presence of ‘tet’ spell?
- Mother should take the baby in lap or keep him in bed at knee chest posture. Bending at knee and hip helps the child in improving the blood flow to the lungs. Baby must be taken to the hospital as he would need sedation, intra venous fluid, oxygen, drugs like betablocker infusion and sometimes ventilator support. A baby with the predisposition must be given iron to keep hemoglobin above 13 gm/dl, must be on regular betablockers. A single episode of spell in absence of any other factor like anemia, dehydration or fever is an indication for surgery.
- What one must do in presence of ‘tet’ spell?
- Why the tetralogy of Fallot occur? How we can prevent it?
- The cause is usually unknown. Genetic factors can sometimes play a role. The consanguinity may play a major role in exposing the disease in genetically predisposed population. The drugs, radiation or some other factors also have some role to play. The fetal echo done at early gestation and early detection of disease may play some role in management.
- Why the tetralogy of Fallot occur? How we can prevent it?
- Is natural or medical cure is possible in TOF patients?
- No. TOF is essentially a complex disease and unlike the VSD, ASD or PDA natural process cannot heal it. The medical therapy is to support the baby from the ill effects of physiological response of body like use of beta blockers. But they are not curative.
- Is natural or medical cure is possible in TOF patients?
- Why the un-operated TOF babies have higher risk for long term problems?
- TOF patients are essentially lacking in adequate oxygen supply in relation to the demand. Hence there growth, development and exercise capacities are grossly abnormal. Not uncommonly, there may be neurological problems secondary to transfer of infective embolus from right side to the brain. Babies with thickened blood (polycythemia) may also have neurological problems.
- Some babies may have associated chromosomal anomalies or involvement of other organs like kidneys and may suffer because of that also.
- Why the un-operated TOF babies have higher risk for long term problems?
- Is surgical correction is unavoidable?
- In absence of natural cure and an effective medical therapy, surgical correction is mandatory.
- Is surgical correction is unavoidable?
- Can surgery be performed in a single stage?
- Typically, the single staged surgical correction of TOF for a classical anatomy done around fifth months or above in our country with good long term results. If baby is symptomatic early or some variations in anatomy exist, the two staged surgery can be planned.
- Can surgery be performed in a single stage?
- What is the palliative surgery for the TOF? What is the Blalock – Taussig shunt?
- As explained before in certain circumstance, palliative surgery is planned as a first stage surgery. This is done by putting an alternative channel from systemic artery to lung artery to improve the blood supply of lung. This is also known as modified Blalock – Taussig (BT) Shunt. In later stage when total correction is achieved, this shunt is closed surgically.
- What is the palliative surgery for the TOF? What is the Blalock – Taussig shunt?
- Can the shunt surgery abolish the blueness of body completely?
- Shunt surgery is done to optimize the systemic saturation at or above 80%. Hence complete abolition of cyanosis is not the goal. If we try to achieve a higher saturation by putting a larger shunt we can harm the lungs by causing flooding of lungs (Pulmonary edema).
- Can the shunt surgery abolish the blueness of body completely?
- For how long a shunt can work?
- A shunt has limited duration of functioning. The size of shunt is weight appropriate and as the weight and accordingly blood volume of baby increases, efficiency of shunt goes down. Therefore baby outgrows the shunt. Sometimes shunt may get blocked particularly in smaller babies.
- For how long a shunt can work?
- What are the precautions to be taken for the babies with modified BT shunt?
- These babies are kept on small doses of aspirin, a known antiplatelet drug. It helps in decreasing the chance of clot formation inside the shunt. Proper hydration must be maintained for these babies, particularly during the episodes of the diarrhea and fever. Time to time pediatrician / cardiologist’s consultation must be taken to know about the proper functioning of shunt. Routine saturation monitoring with pulse oxymeter and hematocrit levels are good indicator of status of shunt. Sudden deepening of cyanosis, distress and cranky child must be attended in emergency and shunt failure must be suspected.
- What are the precautions to be taken for the babies with modified BT shunt?
- What is the corrective surgery foe the TOF?
- The corrective surgery of TOF is done as an open heart procedure on bypass machine. The VSD is closed by sewing in an artificial material -Dacron patch, and by ressecting the muscle of RV out flow. Mostly, a patch is put across the RVOT and its valve. Pulmonary valve is deformed and is removed in most of the cases. In severe TOF with inadequate lumen of main pulmonary artery and its branches, a patch repair is done.
- What is the corrective surgery foe the TOF?
- What is the conduit repair of TOF?
- In cases where RVOT is not repairable, an artificial valve with a tubular structure resembling the RVOT is sewn between the RV and pulmonary artery. This is known as conduit. Usually in these babies initial palliative surgery is done and subsequently after 2 years of age conduit repair is planned. Conduit surgery has disadvantage as more reintervention may be needed.
- What is the conduit repair of TOF?
- How much time is taken for the surgery? How much blood is needed?
- The usual operating time for the TOF is 3-4 hours. Usually, the donation of 4-6 units of blood is required before the surgery. Nowadays blood of any group can be donated and hospital can arrange the appropriate blood group. Specific blood group donors are required in cases of rare blood group or when fresh blood is needed.
- How much time is taken for the surgery? How much blood is needed?
- What is the role of repeat echocardiography in management of TOF?
- The primary diagnosis of TOF is done by echocardiography. Once the primary diagnosis is made, the follow up echocardiography is important in deciding the timing of intervention.
- What is the role of repeat echocardiography in management of TOF?
- What is the role of CT angiography in TOF?
- For an excellent surgery, prior detailed information regarding the lesion must be given to the surgeon by all possible means. CT angiography has helped greatly in presurgical evaluation of lung arteries and anomalous arteries like aorto-pulmonary collaterals in less amount of time. It can be used judiciously whenever required.
- What is the role of CT angiography in TOF?
- What is the role of conventional angiography in TOF?
- The CT angio can provide anatomical details but we cannot get hemodynamic data or chance for intervention. The conventional angiography provides us exactly that. In many patients the abnormal channels can be closed in cath lab before the surgery or sometimes after the surgery. Some residual lesions can also be handled in the cath lab.
- What is the role of conventional angiography in TOF?
- What is the role of ECG and X-ray chest in TOF babies?
- The base-line ECGs and X-rays are required in all babies. These simple investigations provide enormous information to attending physician. They also help in post op patient’s long term follow up.
- What is the role of ECG and X-ray chest in TOF babies?
- What are the chances of getting re-interventions after the corrective surgery of TOF?
- The baby may need reintervention in immediate post op period or later. Immediate interventions are done either for residual holes or RVOT obstruction. There might be some other indications also. Pacemaker implantation can also be needed in an operated TOF. Late interventions are done for residual holes, RVOT obstruction or lung artery stenosis. An important cause of intervention is presence of severe pulmonary leak causing RV dilatation and dysfunction. In grown-up children nowadays, pulmonary valve implantation is done per-cutaneously or by surgery.
- What are the chances of getting re-interventions after the corrective surgery of TOF?
- What is the prognosis of un-operated TOF Babies?
- The longevity of TOF patients is better amongst the other cyanotic cardiac ailments. But quality of life as a rule is not good. These kids are prone for morbidity and mortality as mentioned above.
- What is the prognosis of un-operated TOF Babies?
- What is the prognosis of operated TOF Babies?
- Timely operated TOF babies enjoy a good life and can carry on their profession as well as married life efficiently. Few of them may need some medications. However, sudden life threatening events due to arrhythmias is prevalent in this population. There is some restriction on athletic activities.
- What is the prognosis of operated TOF Babies?
- How often an operated TOF must go for a follow-up check-up?
- Usually first few follow-up are planned more frequently like 15 days, 1month, 3 months then 6 months. Later these visits can be reduced to 1-3 year depending on the follow-up findings.
- How often an operated TOF must go for a follow-up check-up?
- What are the recommendations for live vaccination in these kids?
- According to current norms followed by various tertiary centres world over- no specific protocol to be followed for closed heart shunt procedures. Live vaccines are to be avoided for 4-6 weeks in case of open heart surgery.
- What are the recommendations for live vaccination in these kids?
- What are the recommendations for endocarditis Prevention in operated TOF babies?
- A lifelong endocarditis prophylaxis is recommended for these patients!
- What are the recommendations for endocarditis Prevention in operated TOF babies?
- Is pregnancy is contraindicated in operated TOF patients?
- Once the TOF is repaired successfully, the risk with pregnancy is very low. The risk from a pregnancy goes up if there’s a residual lesion
- Is pregnancy is contraindicated in operated TOF patients?
If you are really seeking Tetralogy of Fallot Surgery, kindly fill up the form for a free consultation with our expert cardiologists. You will be provided with thorough analysis and suggestions regarding the Tetralogy of Fallot Surgery you are seeking for.
Click to Here Fill up our Enquiry Form